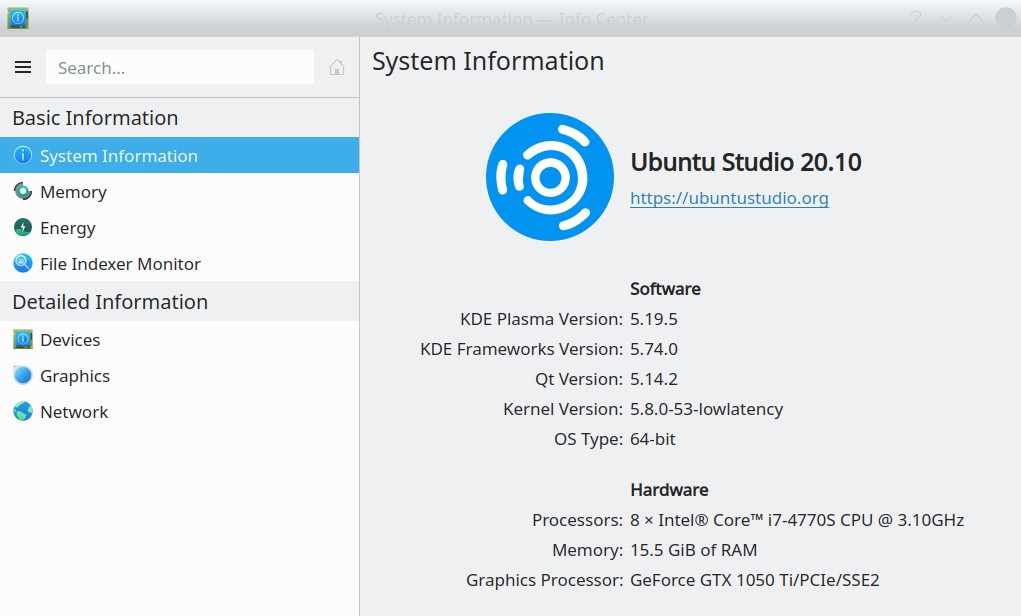
From the Garmin website forum, with button names adjusted for Forunner 45S.
Garmin Forerunner 45S watch stuck in loop with triangle showing on display. Holding LIGHT button for 15 seconds to power off, then pushing LIGHT button to power on doesn’t fix it. To do a hard reset, hold LIGHT button for 15 seconds until the watch powers off. Then hold both the START|STOP and BACK buttons. With these buttons still depressed, press and hold the LIGHT button. After the first beep. release START|STOP. After the second beep, release BACK.